How To Install PulseAudio Equalizer On Linux And Improve Sound
The sound system on Linux is decent, but not the best. That’s why we’ve decided to go over some ways you can easily improve your Pulse Audio sound by adding a system-wide equalizer. The easiest way to add an equalizer is to install PulseAudio Equalizer on Linux. We’re going to cover in detail how you can install it and go over ways you can more easily manage the Linux sound system.
SPOILER ALERT: Scroll down and watch the video tutorial at the end of this article.
PulseAudio Equalizer On Linux
A great way to improve the overall sound quality on Linux is to install an equalizer however equalizer built into the music player isn’t enough. Instead, there is a different solution: Pulse Audio Equalizer. It allows the user to have a system-wide equalizer for all audio coming in and out of the system. This means that no matter what you’re listening to, be it music, videos, or human voices, you’ll be able to easily tweak it.
Getting the equalizer working is easy, and it starts with installing it to the system. Due to the fact that Pulse is open code, a lot of plugins and add-ons have been developed over the years. The equalizer is probably the must used. As a result, many Linux distributions choose to ship it (in some form or another). Here’s how to install it.
Ubuntu
sudo apt install pulseaudio-equalizer
Debian
sudo apt-get install pulseaudio-equalizer
Arch Linux
sudo pacman -S pulseaudio-equalizer
Fedora
sudo dnf install pulseaudio-equalizer
OpenSUSE
The SUSE build service makes installing the equalizer quite easy. Head over to this page and click the 1-click install button. The software supports all current versions of the equalizer.
Other Linuxes
Unfortunately there isn’t much in the way of source code for this Pulse Audio plugin. As a result, you’ll have to look hard in your version of Linux for the equalizer. There are some project files on Launchpad, that users can take apart, but good luck. If you want a good system-wide equalizer, best to use one of the Linux distributions listed above.
Using The Equalizer
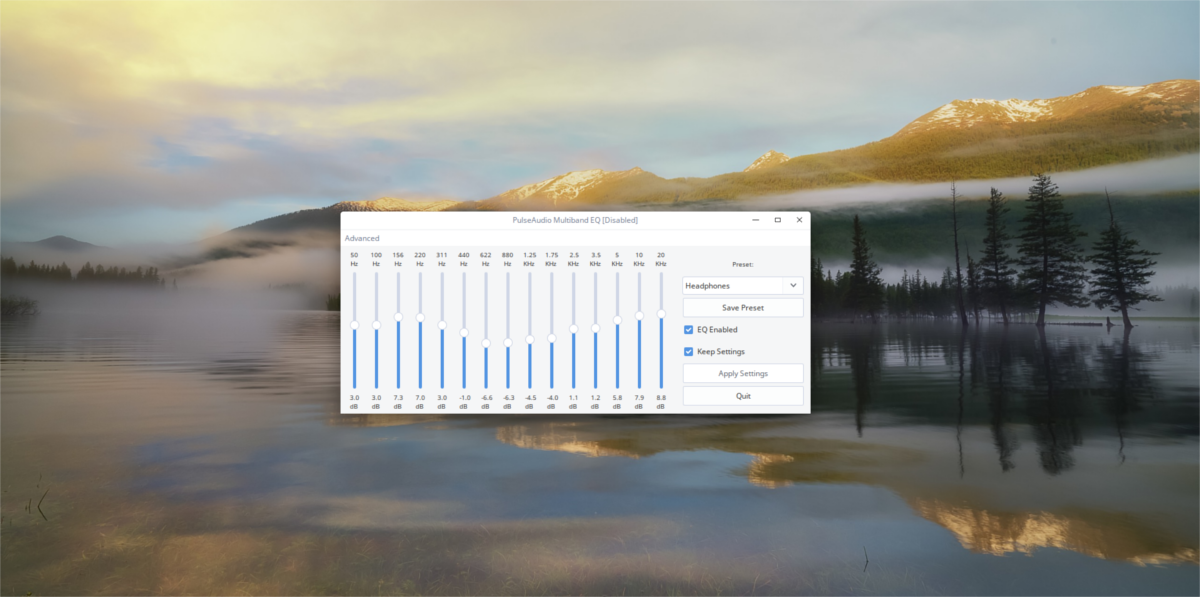
After the equalizer is on the system, simply open your application menu and search for “equalizer”, or “pulse audio equalizer”, and launch it. When it opens, you’ll notice it looks just like any other software equalizer out there. Complete with sliders, and presets. Click the preset menu and sort through the different EQ setups. These can be changed at any time.
To enable the EQ, check the box “EQ enabled”. In addition, make the EQ run at all times by checking the “Keep Settings” box. Lastly, click the “Advanced” button to access advanced settings.
Note: when a user moves the sliders up and down, the label of the EQ will change from the preset name, to “custom”. Save any custom preset by clicking “save preset”.
Quick Pulse Audio Tip
With the Equalizer installed, the Linux audio system is much better. Still, Pulse Audio is a very confusing tool, and as it stands not many users know how to easily manipulate it. That’s why, in this section, we’re going to talk about a tool anyone can install to easily take control of the complex Linux audio system. It starts by installing the Pavucontrol tool.
It’s a graphical control tool for the Linux audio system. With it, users can do all sorts of things.
Ubuntu
sudo apt install pavucontrol
Debian
sudo apt-get install pavucontrol
Arch Linux
sudo pacman -S pavucontrol
Fedora
sudo dnf install pavucontrol
OpenSUSE
sudo zypper install pavucontrol
Other Linuxes
The Pavucontrol tool is easily found on many Linux distributions under the package name “pavucontrol”. Open your package manager and search for that, or something similar like “pulse audio control”.
Usage
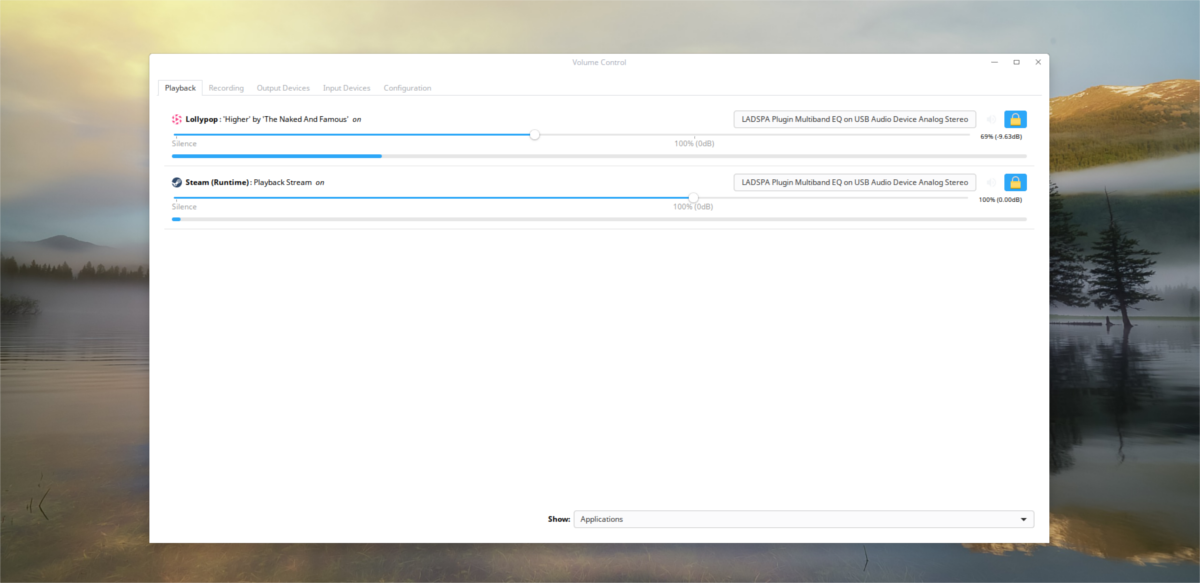
Inside Pavucontrol, there are five tabs; “playback”, “recording”, “output devices”, “input devices”, and “configuration”. To start off, the playback tab represents any program currently using the pulse audio sound system. Control the volume of the playback of each program in this tab.
If you’ve got multiple audio devices, select the audio device label, and click it to swap to a different device.
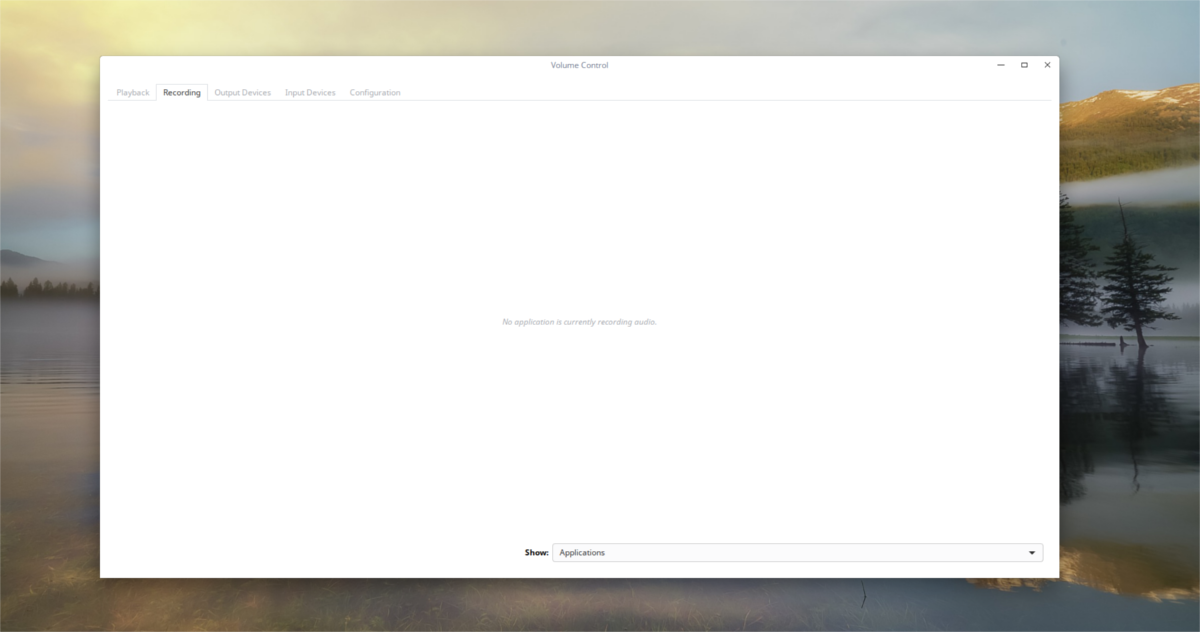
In the recording tab, things are very much the same. Instead of showing playback, it shows all programs currently recording audio. Use the volume sliders to manage how loud the input volume is. Click the audio device label to switch what device Pulse uses to record with.
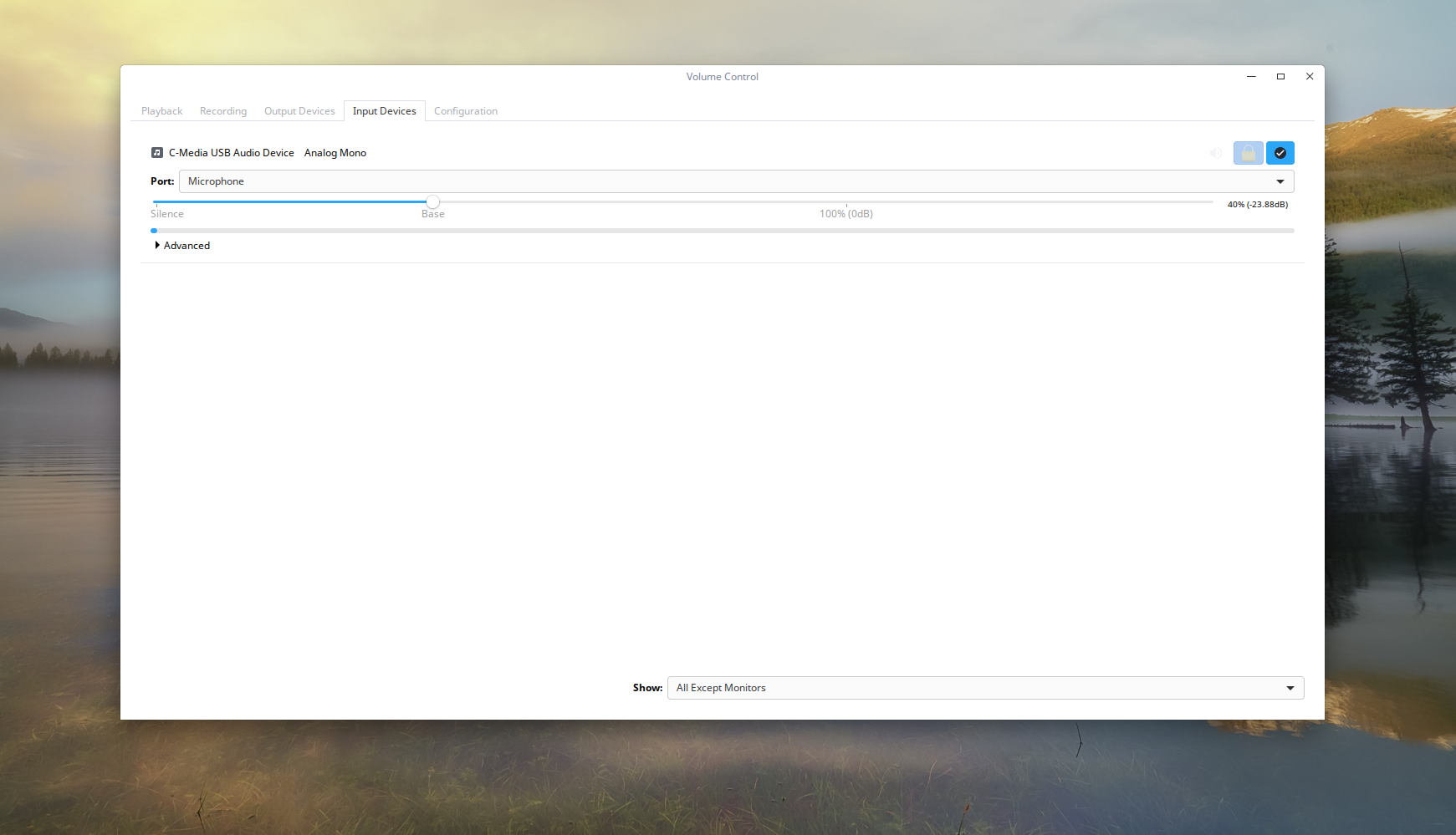
The next tab is “input devices”. This tab allows users to manage the volume of each individual microphone, and device set up for recording.
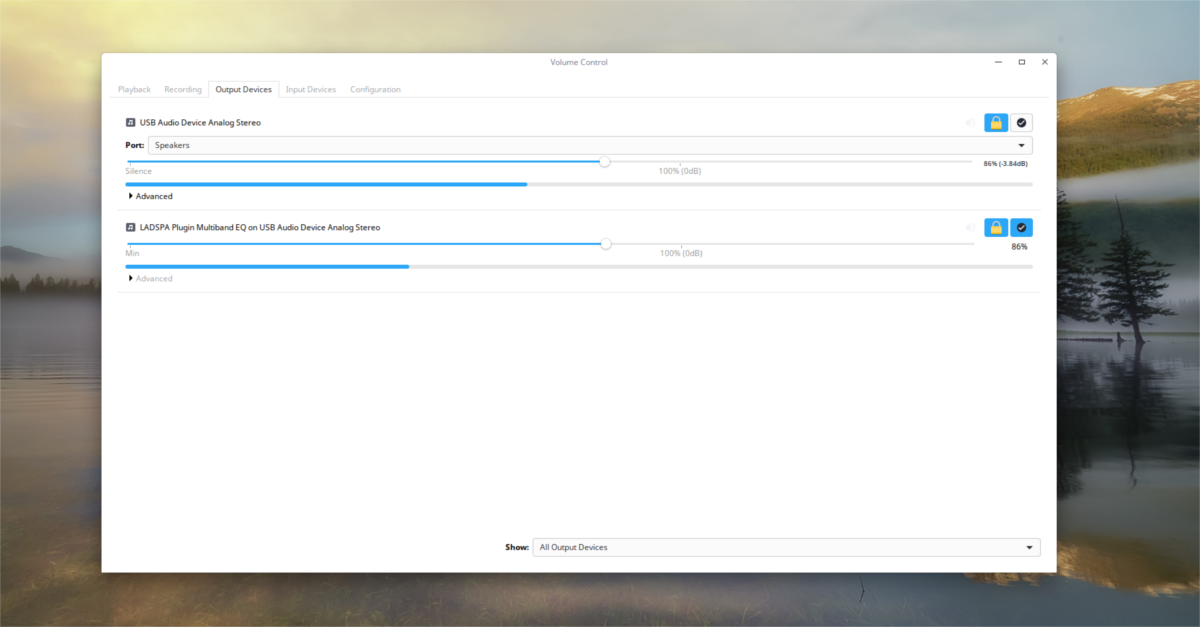
The “output” tab is similar to the “input” tab. Like the input section, output allows the user to easily manage the volume of playback devices individually.
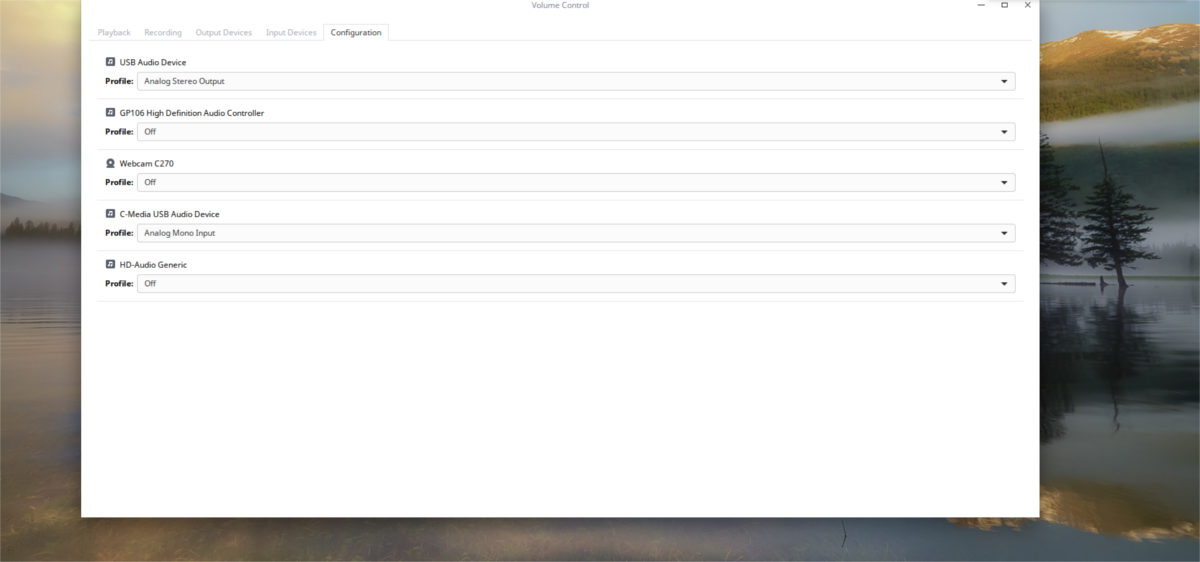
Lastly, the configuration section shows all of the audio equipment. In this section, users can easily turn on and off individual speakers, microphones and etc. To set a device as default, click the “fallback button”. Doing this makes this audio device the default, above all others.
Conclusion
The Pulse Audio sound system has long been the enemy of the Linux community. For years, users have been battling with it, and fighting the sound system just to get decent audio on Linux. 13 years later, it’s much less prone to crashing and overall is a good system.

Thanks
I installed pulse effecf and sound much better with many option for sound quality adjustment
unfortunately
sudo apt-get install pulseaudio-equalizer
does not work
I ran my package manager and it is NOT there
I am using Linux Mint, Ubuntu based
newer versions of Ubuntu for some reason no longer have this
The article is useless and out of date because PAE does not install on Ubuntu 18.04 .
sudo apt install pulseaudio-equalizer does not install this.
You are wrong as of writing this comment. It installs just fine
In Arch Linux I could not find the equalizer just by installing the mentioned package… also i had to install
pulse-audio-gtk and it worked like a charm
You need to run qpaeq
It would’t work in Raspbian? After ‘sudo apt-get install pulseaudio-equalizer’ nothing appeared in my application menu, after ‘sudo apt-get install pavucontrol’ I got ‘PulseAudio Volume Control’ in the Menu but with no EQ. Typing ‘alias eq=’qpaeq’ brought no reaction of the system, and after ‘qpaeq’ I received : There was an error connecting to pulseaudio, please make sure you have the pulseaudio dbus module loaded, exiting… Any decisions how to overcome this?
I totally agree with wegrwegew’s comment. I installed as suggested, however I cannot open the equalizer or find it in the application menu. Does anyone have a solution? Thanks!
Try opening it with the command line, via terminal.
Thanks Mr Gentoo. Although I can get pulseaudio to autocomplete, I can’t get anything along the lines of pulseaudio-equalizer or equalizer or anything.
qpaeq
Not intuitive naming.
Thank you Fetor Flank, kind of difficult name to type!
alias eq=’qpaeq’
It says:
/$ qpaeq
Gtk-Message: 19:09:04.33 Failed to load module “canberra-gtk-module”
There was an error connecting to pulseaudio, please make sure you have the pulseaudio dbus module loaded, exiting… I’m having a hard time with linux why can’t it just be install button then accept accept yes yes done ?
wrgwergew