What RAM Do I Have? How to Check Your Computer’s Memory
Knowing the RAM type is crucial when upgrading your computer’s memory. Luckily, you don’t need to crack open your computer to find this out. Windows comes equipped with several built-in programs, and there are also third-party apps available that can easily get this information for you. Even if you’ve never delved into the specifics of your computer memory before, how to check what RAM you have is a simple task.
How to Check Your RAM Type by Using Third-Party Tools
In addition to Windows tools are third-party programs that show the RAM type. We especially like Speccy because it’s easy to use and shows lots of other useful information about the inside of your PC that you might need.
But other programs can dig up RAM info, too, like HWiNFO and CPU-Z. Here’s how to use these apps to check RAM:
To check your RAM type using CPU-Z:
- Download and install CPU-Z.
- Run CPU-Z.
- Select the Memory tab.
- Look at the Type field. It will tell you if your RAM is DDR3, DDR4, DDR5, or another type of RAM.
Here’s how to check the RAM type using HWiNFO:
- Download and install HWiNFO, and then open the program. There’s a portable option through that link if you’d rather not install it.
- Select Start on the first screen.
- Expand the Memory section on the left.
- Choose a memory module, or select whatever is listed if you only see one.
- Look at the Module Type line to find your RAM type. You can see in our example that the memory type is DDR4 SDRAM.
How to Check Your RAM Speed Using Task Manager
Task Manager provides useful system information, including your RAM speed. Follow these steps to check your RAM speed in Windows 11:
- Open Task Manager by right-clicking the taskbar and selecting Task Manager.
- Go to the Performance tab from the left menu. It’s the second from the top if you don’t see the word.
- Select Memory.
- Your RAM speed is displayed under the memory graph, along with other details like usage, how many RAM slots are used, and form factor.
How to Check Your RAM Speed Using Command Prompt
You can also use Command Prompt to find RAM information in Windows 11. The details here are a bit cryptic compared to what you see in Task Manager, but you’ll get a bit more information.
- Open Command Prompt. Windows 11 might launch Terminal, but it’s the same thing.
- Copy this: wmic memorychip get BankLabel, DeviceLocator, MemoryType, TypeDetail, Capacity, Speed
- Right-click in Command Prompt to paste it.
- Press Enter to run the command to list your RAM information.
What Does the RAM Type Mean?
Now you know your RAM type, but have you ever wondered how it stacks up against others? Here’s a quick look at the different types of memory modules commonly found in computers:
- DDR (Double Data Rate): DDR RAM is the basic type of memory used in older systems. It transfers data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal, which doubles the data rate compared to its predecessor, SDR (Single Data Rate) RAM.
- DDR2 (Double Data Rate 2): DDR2 RAM improved upon DDR by offering higher data transfer rates and lower power consumption. It operates at higher clock frequencies and uses a different pin configuration than DDR.
- DDR3 (Double Data Rate 3): DDR3 RAM further enhanced data transfer speeds and energy efficiency compared to DDR2. It introduced features like higher bus frequencies and reduced voltage requirements to make it suitable for modern computing needs.
- DDR4 (Double Data Rate 4): DDR4 RAM is the successor to DDR3 and provides even faster data transfer rates and lower power consumption. It offers increased memory module capacities, improved reliability, and enhanced performance for demanding applications and gaming.
- DDR5 (Double Data Rate 5): DDR5 RAM is the latest standard, offering significant improvements over DDR4. It boasts higher data transfer rates, increased memory density, and improved power efficiency. DDR5 is designed to meet the requirements of emerging technologies like 5G and AI.
- SODIMM (Small Outline Dual Inline Memory Module): SODIMMs are a smaller form factor of memory modules commonly used in laptops and small form factor computers. They come in the same DDR, DDR2, DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5 variants as DIMMs but are designed to fit into smaller spaces, making them ideal for portable and space-constrained devices.
If your computer is sluggish, slow RAM could be partially responsible. You can overclock your RAM to make it faster for multitasking.
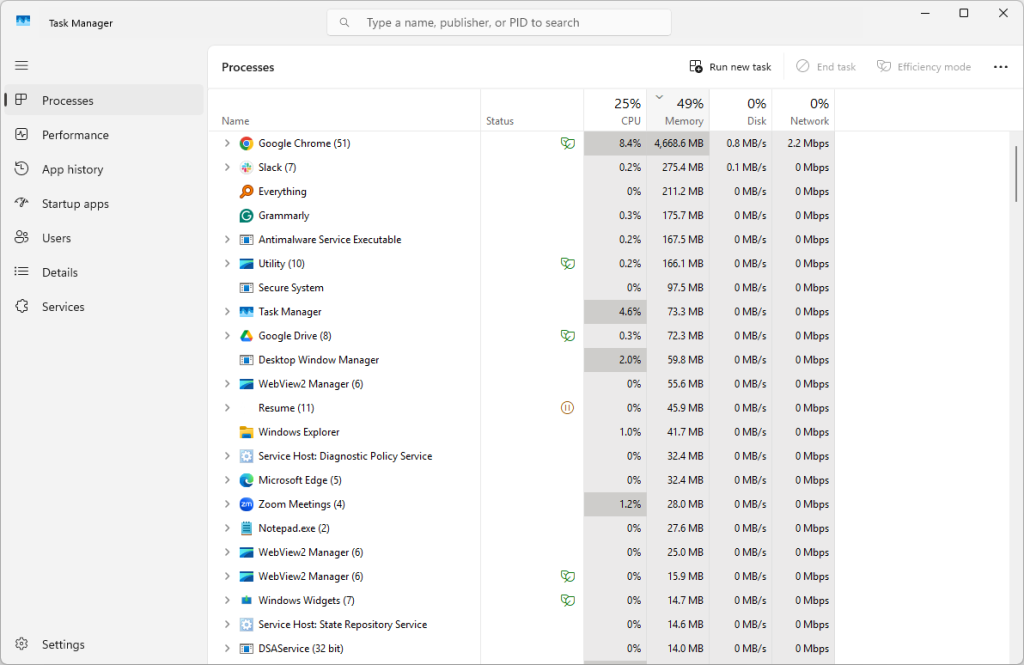
How to Use Task Manager to Find Apps Using Lots of RAM
Task Manager is incredibly handy for taking a glimpse at what’s happening on your computer. You already learned above how to use this tool to see your RAM speed. Now, let’s walk through how to use Task Manager to list all the top RAM hogs.
- Open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc.
- Ensure the Processes tab is selected on the left.
- On the right, select Memory at the top to sort the list by whatever is using the most (or least) memory. If the first few entries say 0 MB, select the column heading again to reverse the order.
- Listed near the top of the list are all the apps using the most RAM. This list can change over time, and you’ll even notice it fluctuate in real-time.
Tip: Right-click one of these memory hogs and select End task to shut it down. Depending on the amount of RAM it was using, you could feel performance gains instantly.
How to Optimize RAM Automatically
Computers commonly run into memory-related issues, especially over time, as we add more and more software to them. You can see in Task Manager that a computer has a finite amount of physical RAM to use for these apps. Approach that maximum memory usage, and you’ll start to experience programs crashing, apps failing to install, and other strange glitches.
This is where a RAM optimization tool comes in. This kind of program will monitor your RAM usage in real time and make smart changes to how your programs use the memory so that the hardware is there when you need it most.
Microsoft PC Manager is one such program. It’s 100% free and easy to use. We like this option because of its extensive toolset that most other RAM optimization tools just can’t match. You get all the following:
- Heath check: Recommends which startup apps to turn off and which ones to enable, and can instantly disable third-party taskbar extensions for boosted security.
- Process manager: Get a list of high-RAM apps with a convenient End button available to instantly shut them down and free up RAM.
- Deep cleanup: Scan system items, app items, computer usage traces, Recycle Bin, and other areas for junk files taking up unnecessary disk space. In our tests, PC Manager recommended cleaning 10 GB of useless data!
- Startup apps: Toggles to quickly disable startup apps to speed up your computer’s boot-up time.
- Storage management: View all your downloaded files, large files, and duplicate files for an overview of what’s taking up all your hard drive space.
- Deep uninstall: Delete apps and also remove their residual files and registry entries for a full removal.
- Toolbox: Shortcuts to various Windows tools, including the screenshot utility, Notepad, Recorder, and even web tools like a currency converter and image search engine.
The RAM optimization feature, called Smart Boost, will automatically boost your PC when it detects high RAM usage. Here’s how to trigger a RAM boost manually and how to set up the program to do so automatically when your PC needs it most:
- From the Home tab, select Boost. This will instantly free up the necessary system resources to help your computer fun better.
- To avoid having to do this manually, select Set Smart boost.
- Select the toggle under Smart boost setting to switch it on.
Tip: Turn on the Start PC Manager automatically option to ensure that the RAM-boosting capabilities are always ready to be triggered, even if you reboot your PC.
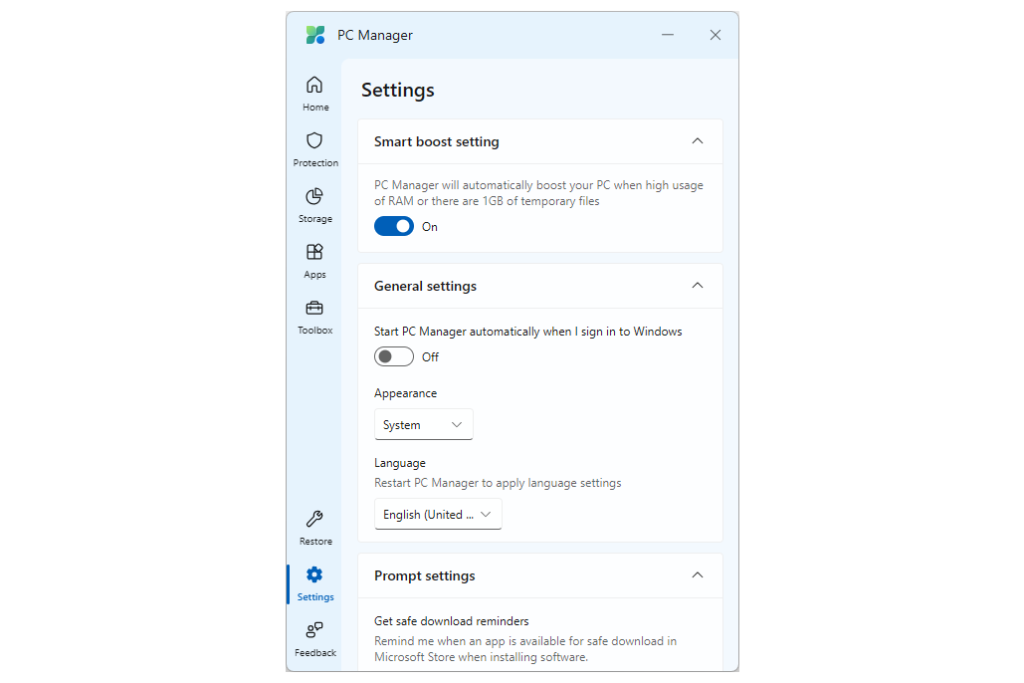
Now, when PC Manager detects high memory usage or an excess of temporary files, it will trigger this automation. Your computer will always work in tip-top shape, even if you forget that this handy software is installed.
